JavaScript is the programming language of the Web
JavaScript is a high-level, often just-in-time compiled language that conforms to the ECMAScript standard.[10] It has dynamic typing, prototype-based object-orientation, and first-class functions. It is multi-paradigm, supporting event-driven, functional, and imperative programming styles. It has application programming interfaces (APIs) for working with text, dates, regular expressions, standard data structures, and the Document Object Model (DOM)

The first popular web browser with a graphical user interface, Mosaic, was released in 1993. Accessible to non-technical people, it played a prominent role in the rapid growth of the nascent World Wide Web. The lead developers of Mosaic then founded the Netscape corporation, which released a more polished browser, Netscape Navigator, in 1994. This quickly became the most-used.
During these formative years of the Web, web pages could only be static, lacking the capability for dynamic behavior after the page was loaded in the browser. There was a desire in the flourishing web development scene to remove this limitation, so in 1995, Netscape decided to add a scripting language to Navigator. They pursued two routes to achieve this: collaborating with Sun Microsystems to embed the Java programming language, while also hiring Brendan Eich to embed the Scheme language.
JavaScript Can Change HTML Content
getElementById()
JavaScript Where To
<script>
</script>Example

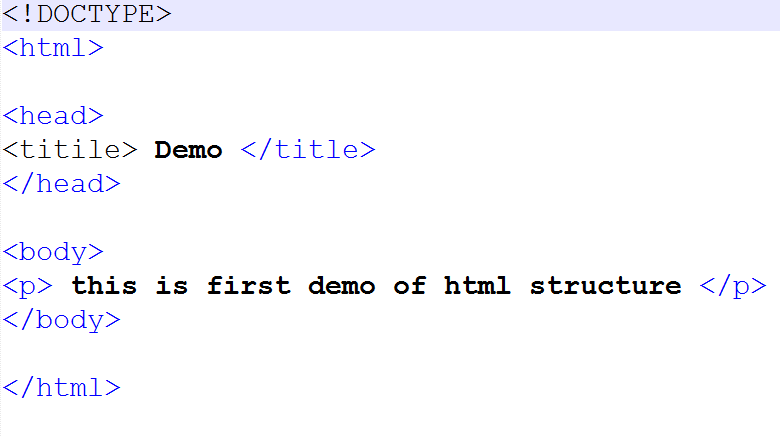
A Simple HTML Document
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages
HTML describes the structure of a Web page
HTML consists of a series of elements
HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
HTML elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is a link", etc.
HTML Documents
All HTML documents must start with a document type declaration: <!DOCTYPE html>.
The HTML document itself begins with <html> and ends with </html>.
The visible part of the HTML document is between <body> and </body>.
HTML Headings
HTML headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags.
<h1> defines the most important heading. <h6> defines the least important heading:
HTML Paragraphs
HTML paragraphs are defined with the <p> tag:
HTML Links
HTML links are defined with the <a> tag:
HTML Images
HTML images are defined with the <img> tag.
The source file (src), alternative text (alt),
width, and height are provided as attributes:
HTML
All HTML documents must start with a document type declaration: <!DOCTYPE html>.
The HTML document itself begins with <html> and ends with </html>.
The visible part of the HTML document is between <body> and </body>.
HTML Headings
HTML headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags.
<h1> defines the most important heading. <h6> defines the least important heading:
HTML Paragraphs
HTML paragraphs are defined with the <p> tag:
HTML Links
HTML links are defined with the <a> tag:
HTML Images
HTML images are defined with the <img> tag.
The source file (src), alternative text (alt),
width, and height are provided as attributes:
HTML Attributes
All HTML elements can have attributes
Attributes provide additional information about elements
Attributes are always specified in the start tag
Attributes usually come in name/value pairs like: name="value"
The href Attribute
The <a> tag defines a hyperlink. The
href attribute specifies the URL of the page
the link goes to:
The src Attribute
The <img> tag is used to embed an
image in an HTML page. The src attribute
specifies the path to the image to be displayed:
The width and height Attributes
The <img> tag should also contain the
width and
height attributes, which specify the width and
height of the image (in pixels):
The alt Attribute
The required alt attribute for the <img>
tag specifies an
alternate text for an image, if the image for some reason cannot be displayed.
This can be due to
a slow connection, or an error in the src attribute, or if the user uses a screen
reader.
The style Attribute
The style attribute is used to add styles to
an element, such as color, font, size, and more.
The required alt attribute for the <img>
tag specifies an
alternate text for an image, if the image for some reason cannot be displayed.
This can be due to
a slow connection, or an error in the src attribute, or if the user uses a screen
reader.
The lang Attribute
You should always include the lang attribute
inside the <html> tag, to declare the
language of the Web page. This is meant to assist search engines and browsers.
The title Attribute
The title attribute defines some extra
information about an
element.
HTML Headings
HTML headings are titles or subtitles that you want to display on a webpage
HTML headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags.
<h1> defines the most important heading. <h6> defines the least important heading.
Headings Are Important
Search engines use the headings to index the structure and content of your web pages.
Users often skim a page by its headings. It is important to use headings to show the document structure.
<h1> headings should be used for main headings, followed by <h2> headings, then the less important
<h3>, and so on.
Bigger Headings
Each HTML heading has a default size. However, you can specify the size for any heading
with the style attribute, using the CSS font-size property:
HTML Paragraphs
The HTML <p> element defines a paragraph.
A paragraph always starts on a new line, and browsers automatically add some white space (a margin) before and after a paragraph.
HTML Horizontal Rules
The <hr> tag defines a thematic break in an HTML page, and is most often
displayed as a horizontal rule.
The <hr> element is used to separate content (or define a change) in an HTML
page:
HTML Line Breaks
The HTML <br> element defines a line break.
Use <br> if you want a line break (a new line) without starting a new paragraph:
The HTML <pre> Element
The HTML <pre> element defines preformatted text.
The text inside a <pre> element is displayed in a fixed-width font (usually
Courier), and it preserves both spaces and line breaks:
HTML Styles
The HTML style attribute is used to add styles to an element, such as color, font, size, and more.
The HTML Style Attribute
Setting the style of an HTML element, can be done with the style attribute.
The HTML style attribute has the following syntax:
The property is a CSS property. The value is a CSS value.
Background Color
The CSS background-color property defines the background color
for an HTML element.
Text Color
The CSS color property defines the text color for
an HTML element
Fonts
The CSS font-family property defines the font to be used
for an HTML element
Text Size
The CSS font-size property defines the text size for
an HTML element
Text Alignment
The CSS text-align property defines the horizontal text alignment for an HTML element
HTML Text Formatting
HTML contains several elements for defining text with a special meaning.
HTML Formatting Elements
<b>- Bold text<strong>- Important text<i>- Italic text<em>- Emphasized text<mark>- Marked text<small>- Smaller text<del>- Deleted text<ins>- Inserted text<sub>- Subscript text<sup>- Superscript text
The HTML <b> element defines bold text,
without any extra importance.
The HTML <strong> element defines text
with strong importance. The content inside is typically displayed in bold.
The HTML <i> element defines a part of
text in an alternate voice or mood. The content inside is typically displayed in
italic.
The HTML <em> element defines
emphasized text. The content inside is typically displayed in italic.
The HTML <small> element defines
smaller text
The HTML <mark> element defines text
that should be marked or highlighted
The HTML <del> element defines text
that has been deleted from a document. Browsers will usually strike a line
through deleted text
The HTML <ins> element defines a text
that has been inserted into a document. Browsers will usually underline inserted
text
The HTML <sub> element defines
subscript text. Subscript text appears half a character below the normal line,
and is sometimes rendered in a smaller font. Subscript text can be used for
chemical formulas, like H2O
The HTML <sup> element defines
superscript text. Superscript text appears half a character above the normal
line, and is sometimes rendered in a smaller font. Superscript text can be used
for footnotes, like WWW[1]:
Aenean lorem odio, mollis sed consequat et, pellentesque id purus. Nunc sagittis malesuada urna, ultricies lacinia nisi varius vitae. Aliquam sit amet egestas sapien, nec mollis quam.




